 Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
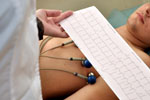
An electrocardiogram records the electrical activity of the heart. Small sticky patches (electrodes) are stuck on to your arms, legs and chest and wires from the electrodes are connected to the ECG machine that reads the heart activity and prints it out on paper. The ECG can show if there is a problem with your heart rhythm or damage to your heart.
 Exercise Stress Test (EST)
Exercise Stress Test (EST)
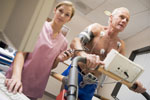
This test checks how the heart responds to exercise. The heart needs more blood and oxygen when you are active and the EST can show if the heart muscle is getting enough blood during exercise.
Small sticky patches (electrodes) are put on your chest and connected by wires to an ECG machine. A blood pressure cuff will be placed on your arm. You will be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike where the incline and speed is increased every few minutes. Your heart’s activity and blood pressure will be recorded while you are exercising.
The amount of exercise you have to do is not as intensive as a gym workout and if you develop chest pain or have changes in your ECG the test will be stopped.
 CT Coronary Calcium Score
CT Coronary Calcium Score
The calcium scoring test is done using a special X-ray (CT scanner) and is a way of measuring how much calcium deposits are in your coronary arteries (normal healthy arteries don’t contain calcium). Atheroma is the name of the calcium-containing deposits that can build up and cause narrowing of your hearts arteries. A score of zero means you have no calcium deposits and it is unlikely that you have heart disease. Having this test does mean that you will be exposed to a small amount of radiation.
 CT Coronary Angiogram
CT Coronary Angiogram
This test is also done using the CT scanner. Before starting this test a special dye (contrast medium) is injected into a vein in your arm to help show the arteries on the surface of the heart that may need further investigation by a heart specialist (Cardiologist).
Having a CT coronary angiogram does mean that you are exposed to some radiation. This test shows the blood flow through the coronary arteries and will show if you have any narrowing in them from calcium deposits. This test is used to describe the amount of calcified plaques in the arteries of the heart and is helpful to identify early onset of heart disease in individuals who have no symptoms.
 Stress Echocardiogram
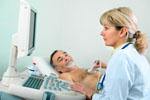
Stress Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is similar to an ultrasound and uses high frequency sound waves to build a detailed picture of your heart when it is under stress either by increasing your heart rate by medication or by exercise. The test helps diagnose heart disease. This test does not use radiation.
 Myocardial Perfusion Scan
Myocardial Perfusion Scan
This test is done in two parts rest and stress:
- Rest – as small amount of radioactive substance (isotope) will be injected into your blood and then a large camera takes pictures of your heart as the isotope passes through the heart while you are resting.
- Stress – to do this part you will be given another isotope injection and asked to exercise on a bike or treadmill (or if you are unable to exercise a medicine may be given to make your heart beat faster and harder). The camera will then take pictures as in part 1 of this test.
The two parts of this test are done on separate days, and this test helps to diagnose heart disease and see how well your heart pumps and how much blood gets to the heat muscle.
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Short burst of magnetic fields and radio waves used during this test produce very detailed pictures of the heart. It shows the structure of your heart and blood vessels and can measure the flow of blood through the heart and the major arteries.
The whole test may take up to an hour and you will need to lie very still during the scan. The advantage of this test is that you will not be exposed to radiation. Patients with pacemakers (unless they have the new MRI-safe pacemaker) or other forms of metal in their body cannot have this test.
 Carotid Ultrasound (CIMT)
Carotid Ultrasound (CIMT)
The carotid artery is in your neck and supplies the blood to the brain. Cholesterol deposits can build up in the artery lining. The carotid ultrasound shows the movement of the blood through your blood vessels and measures the thickness of the inner layer (intima media) of your carotid artery. If the thickness if more that than it should be for your age then this could indicate early cardiovascular disease.
During the test an ultrasound probe is passed over the skin where your carotid artery is located in your neck. Although this test does not look at the arteries that feed the heart, it is considered an indicator of heart disease. It is assumed that if there is disease in the carotid artery there will be disease in the arteries that feed the heart. This test does not use radiation.
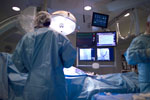 Coronary Angiogram
Coronary Angiogram
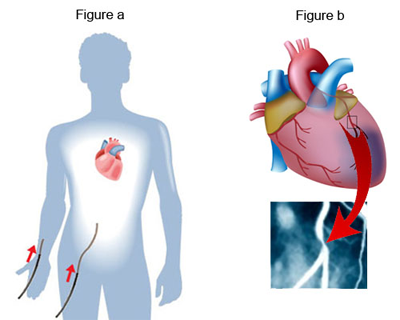
A coronary angiogram is an x-ray procedure which accurately shows the location and severity of all narrowing and blockages in the coronary arteries.
The procedure is performed in a special room (‘cath-lab’) similar to an operating theatre. A small tube, called a catheter is inserted through a small incision, either in the groin or right arm (radial artery). The catheter is moved up through the artery until it reaches the coronary arteries on the surface of the heart (Figure a). A small amount of x-ray sensitive dye is injected and x-rays are then taken as the dye moves through the coronary arteries showing any narrowing or blockages (Figure b).
The procedure takes about 40 minutes. Local anaesthetic is given at the entry site and no pain is felt as there are no nerves inside arteries. There may be a slight sensation when the dye is injected.